|
Symbolic simulation in verification of embedded array
systems and arithmetic unit |
| (The projects
are sponsored by Cadence Design Inc (Verplex group) and
California MICRO program 2001-2004) |
| Embedded memory arrays and
arithmetic units are important components in digital ICs
for most high-performance applications. Both of them
have the difficulties for verification. In our project,
we provide several methods to target them. Enhanced
symbolic simulation based on collapsing and encoding is
one crucial way to avoid the OBDD size explosion, OBDD
partition with functional space decomposition is another
way to improve the symbolic simulation. |
|
|
|
|
Symbolic methods in efficient
validation of embedded memory arrays |
| We incorporate
an ATPG-style decision procedure into the symbolic
simulation. To verify that a design satisfies a given
assertion, the assertion is modeled as a constraint
circuit. ATPG assigns the constant values through the
backward justification, and symbolic simulation can
simulate the sub-assertions with efficient input
encoding. |
|
 Fig.1
Fig.1 |
| For the
content-addressable memory, we explore the similarity of
the word-level functions between the design and
assertions. Some OBDD sub-trees can be collapsed into a
new variable, so the output OBDD sizes are dramatically
reduced during the simulation. |
Publications:
• G. Parthasarathy, M. K. Iyer, T. Feng, L.-C. Wang,
K.-T. Cheng and M. S. Abadir, "Combining
ATPG and Symbolic Simulation for Efficient Validation of
Embedded Array Systems," in Proc. Int. Test
Conf., pp. 203-212, Oct. 7-10, 2002.
• T. Feng, Li-C. Wang, K.-T. Cheng, M. Pandey and M. S.
Abadir, "Enhanced
Symbolic Simulation for Efficient Verification of
Embedded Array Systems," in Proc. Asia and South
Pacific Design Automation Conf., pp.302-307, Jan.
21-24, 2003.
• Li-C. Wang, T. Feng, K.-T. Cheng, M. S. Abadir and M.
Pandey, "Enhanced
Symbolic Simulation for Functional Verification of
Embedded Array Systems," in Design Automation
for Embedded Systems., pp.173-188, 2003. |
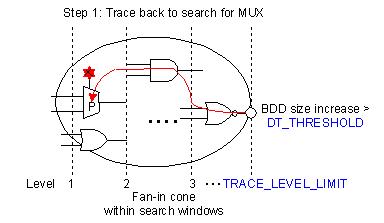
Enhanced Symbolic simulator with functional space
decomposition |
| We use
functional-space decomposition to improve the symbolic
simulator. The datapath and control logic of a circuit
is separated, and their corresponding functions are
recorded in two different domains by a special structure
called 2-tuple list. The functional space in the control
domain can further be decomposed into subspaces during
the simulation to achieve the optimal OBDD size and run
time. |
| Our
decomposition is based on the decision points implicitly
built inside the circuit. We apply some heuristics to
extract and choose the decision points automatically. To
achieve the tradeoff between time and space complexity,
a dynamic heuristic is proposed for choosing the key
partitioning points inside the circuit. The heuristic is
invoked based on the OBDD performance during the
simulation for the reduction of both OBDD size and the
run time. The effectiveness of the approach is
demonstrated on the arithmetic circuits and the memory
management unit. |
|
 Fig
2. Fig
2. |
Publications:
• T. Feng, Li-C. Wang, Kwang-Ting Cheng, "Improved
Symbolic Simulation By Functional Space Decomposition",
in Asia and South Pacific Design Automation Conference
(ASP-DAC), Jan, 2004.
• T. Feng, Li-C.Wang, Kwang-Ting Cheng, C.C.Lin, "Improved
Symbolic Simulation By Dynamic Functional Space
Partitioning", in Design, Automation and Test in
Europe (DATE), Feb, 2004. |
|
|
Project Sponsors |
| (The projects
are sponsored by Cadence Design Inc (Verplex group) and
California MICRO program 2001-2004) |

 |
|
This webpage is
maintained by Tao Feng
tfeng@ece.ucsb.edu,
last updated August 12, 2004.
|
|